Hi! My name is Hashar Mujahid and today we will see how Kerberos authentication works.

What is Kerberos?
Kerberos is an authentication protocol that Microsoft widely implements in their Active Directory Services. It allows users to access services or data over an untrusted network by proving their identity with the help of tickets. All major operating systems like macOS, Linux, etc also support Kerberos.
Why understand Kerberos?
“ If you know yourself but not the enemy, for every victory gained you will also suffer a defeat” (Sun Tzu)
From a penetration tester point of view, almost 90 percent of big companies use Active Directory Environment. And Kerberos is the main authentication system used in AD services. So it is detrimental for every wannabe pentester or red teamer to understand how Kerberos authentication works.
ANATOMY OF KERBEROS AUTHENTICATION.
Now we will see how this authentication system works and what are the components or entities involved in this process.
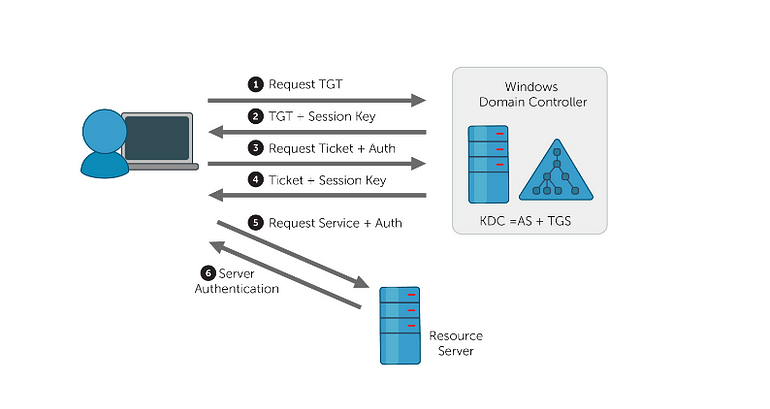
STEP 1: Authentication Server Request (AS-REQ)
Let’s say a client wants to access some resource at the resource server to do that first it needs to send a request to the Key Distribution Center (KDC). This request will contain the NTLM hash of the client’s password and a timestamp encrypted with that NTLM hash. This is to certain that the request is actually coming from a user that it claims to be.
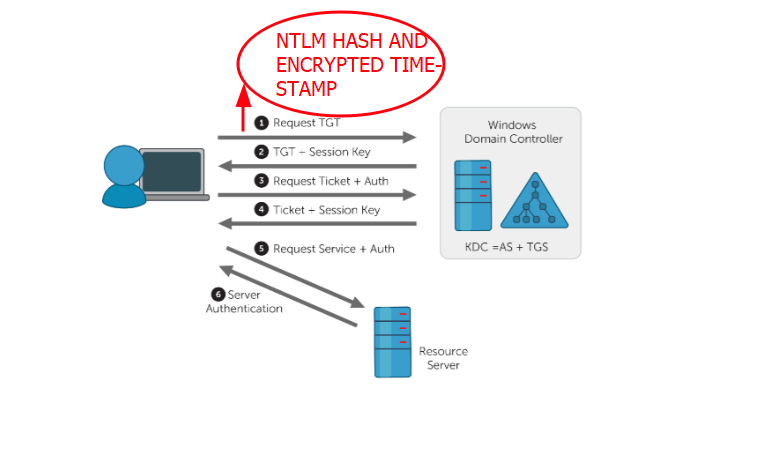
At the end of step one. The KDC receives the request made by the user and decrypts it.
STEP 2: Authentication Server Response (AS-REP)
A key distribution center is composed of essentially 2 components.
- Authentication Server
- Ticket Granting Server
The KDC receives the request made by the user and decrypts it. If the request is validated the KDC responds with the TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket). The TGT is encrypted and signed with the hash of a special account of the domain controller name “KRBTGT”. Only the KRBTGT account can open and read the tickets.
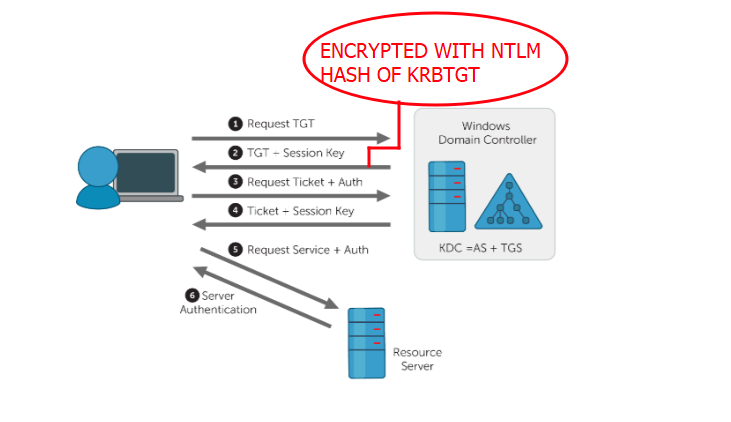
STEP 3: Ticket Granting Service Request (TGS-REQ)
Now the client has a TGT but he cannot decrypt it because it was encrypted using a hash of the krbtgt account. So the client sends back the TGT to KDC and requests a TGS ticket a TGS ticket is a ticket that grants access to a specific service on an AD domain environment. At the end of step 3, the KDC receives the request and Decrypts the TGT. This is the only validation at this step if the TGT is validated the KDC assumes that whatever is returned inside the TGT is valid.
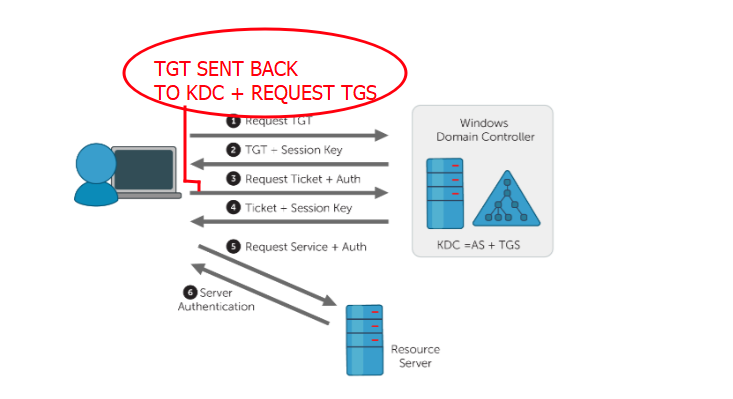
STEP 4: Ticket Granting Server Response (TGS-REP)
Once the TGT is validated the KDC response with TGS. TGS is encrypted using the target server or resource server’s NTLM hash. So that client could not decrypt it only the Resource server could decrypt it.
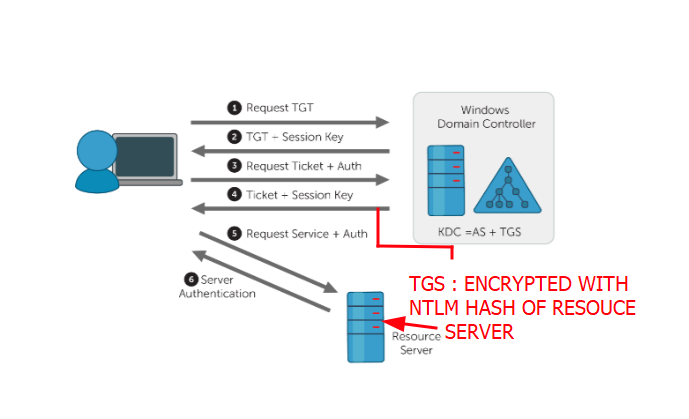
STEP 5: Connect to Resource Server (AP-REQ)
RESOURCE SERVER CAN ALSO BE CALLED AS APPLICATION SERVER
Now the client has a TGS the client or user can connect to the resource server and presents their TGS to the resource server.
STEP 6: Response from the Resource Server (AP-REP)
Now because the TGS is encrypted using the application server or resource server’s NTLM hash. It decrypts it and decides on the privileges of the user whether it can access the service or not.
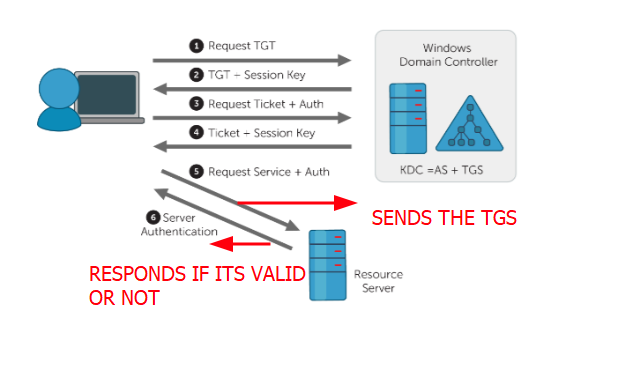
That is all that happens in the Kerberos Authentication protocol.
I hope you understood it. I will be posting more blogs on how to approach an Active Directory environment from a pentester’s point of view If you want to learn more about System and Web application Penetration Testing Consider following me.
I’ll see you in the next blog till then HAPPY HACKING! ❤
